Competition between Bose-Einstein condensation and spin dynamics
We study the impact of spin-exchange collisions on the dynamics of Bose-Einstein condensation by rapidly cooling a chromium multicomponent Bose gas.
arXiv:1607.02406 (2016) / Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 185302 (2016)
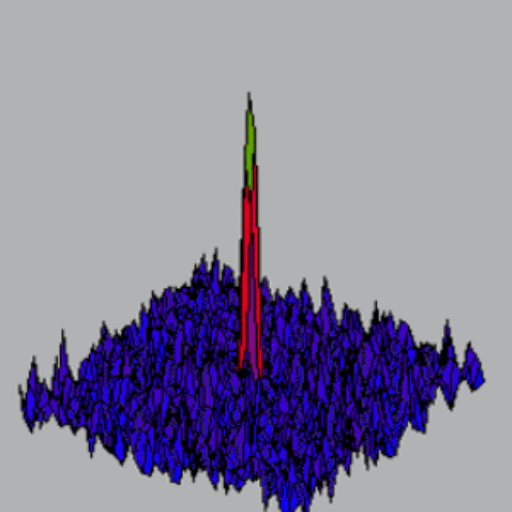
Despite relatively strong spin-dependent interactions, the critical temperature for Bose-Einstein condensation is reached before the spin degrees of freedom fully thermalize. The increase in density due to Bose-Einstein condensation then triggers spin dynamics, hampering the formation of condensates in spin-excited states. Small metastable spinor condensates are, nevertheless, produced, and they manifest in strong spin fluctuations.