Seminar: Laboratoire Charles Fabry, Palaiseau
Quantum magnetism with cold atoms: 1) dissipative cooling of spin chains 2) birth of the strontium experiment at LPL
Cooling all external degrees of freedom of optically trapped chromium atoms using gray molasses
We report on a scheme to cool and compress trapped clouds of highly magnetic 52Cr atoms. This scheme combines sequences of gray molasses, which freeze the velocity distribution, and free evolutions in the (close to) harmonic trap, which periodically exchange the spatial and velocity degrees of freedom.
arXiv:1812.09177 (2018) / Phys. Rev. A 99, 023607 (2019)
Conference: Quantum Technologies Conference IX, Gdansk
Dissipative cooling of spin chains by a bath of dipolar particles
New arrival: Pierre Bataille
Welcome to Pierre Bataille, first PhD on the strontium apparatus!
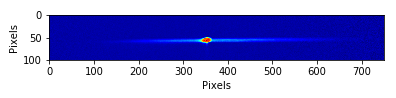
Strontium 88 ODT
Strontium 88 at 500 nK in a crossed dipole trap.
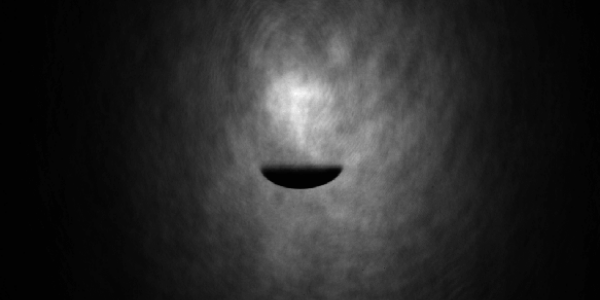
Narrow-line red magneto-optical trap
Narrow-line red magneto-optical trap at about 1 µK, with strontium 88.
Tutorial: Paris center for quantum computing, Paris
Some aspects of quantum simulation using cold atoms
Collective spin modes of a trapped quantum ferrofluid
We report on the observation of a collective spin mode in a spinor Bose-Einstein condensate.
arXiv:1804.10254 (2018) / Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 013201 (2018)
Dissipative cooling of spin chains by a bath of dipolar particles
We consider a spin chain of fermionic atoms in an optical lattice, interacting with each other by super-exchange interactions. We theoretically investigate the dissipative evolution of the spin chain when it is coupled by magnetic dipole–dipole interaction to a bath consisting of atoms with a strong magnetic moment.
arXiv:1803.10663 (2018) / New J. Phys. 20 073037 (2018)
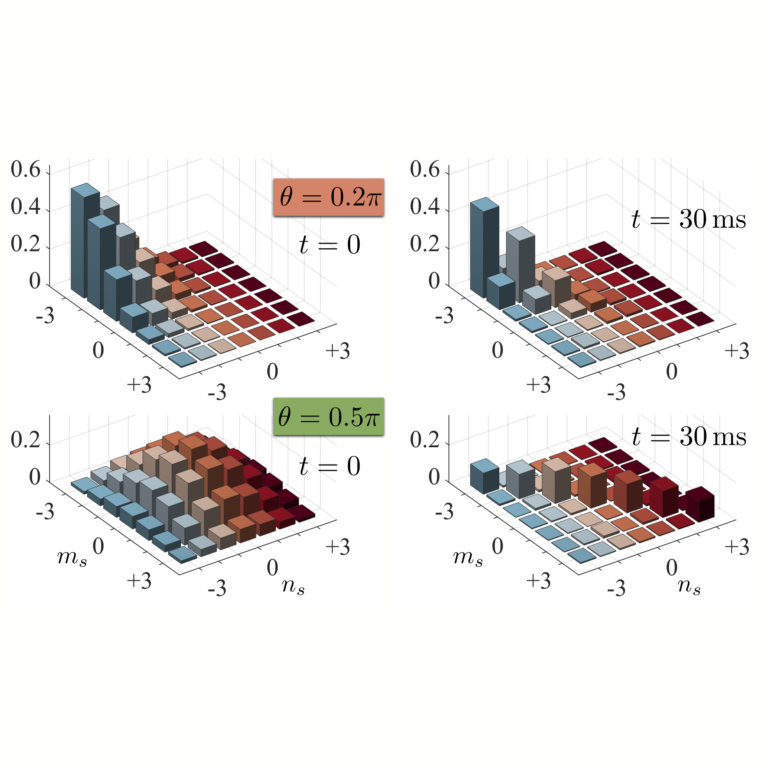
Exploring out-of-equilibrium quantum magnetism and thermalization in a spin-3 many-body dipolar lattice system
We study the spin dynamics and approach towards local thermal equilibrium of a macroscopic ensemble of S = 3 chromium atoms pinned in a three dimensional optical lattice and prepared in a pure coherent spin state, under the effect of magnetic dipole–dipole interactions.
arXiv:1803.02628 (2018) / Nat. Commun. 10, 1714 (2019)